The Plant-Cyclopedia
Select a plant...
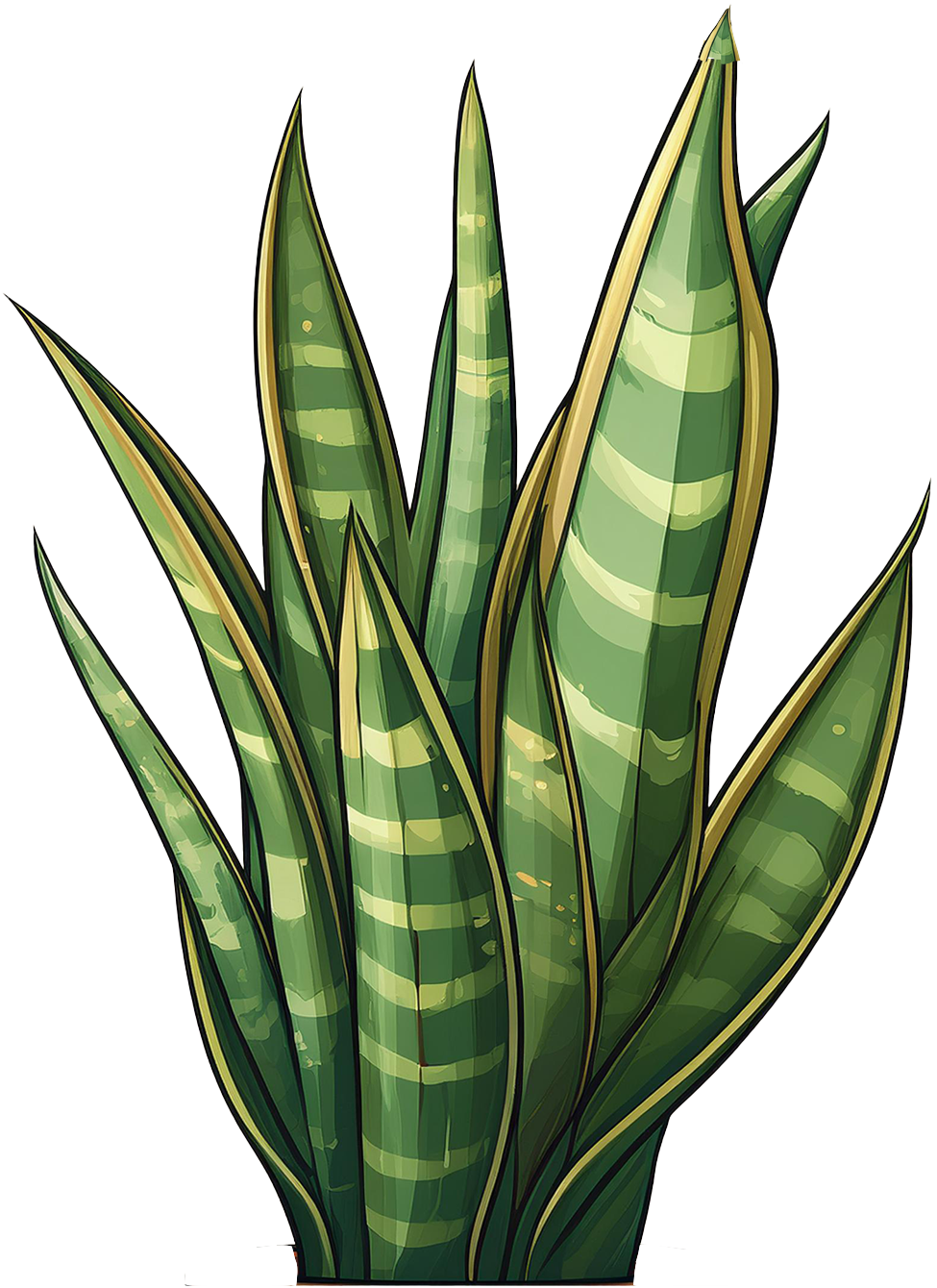
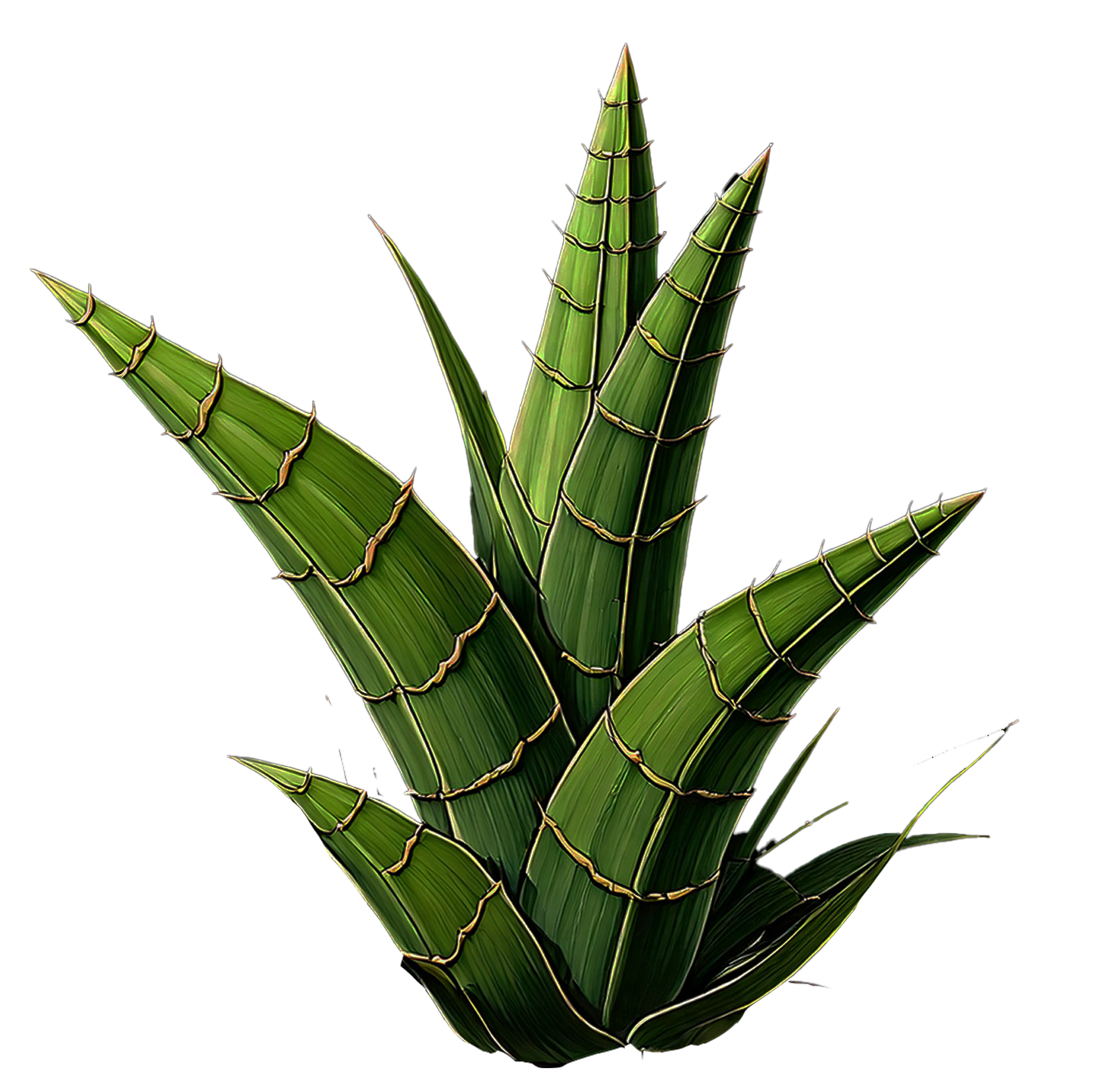
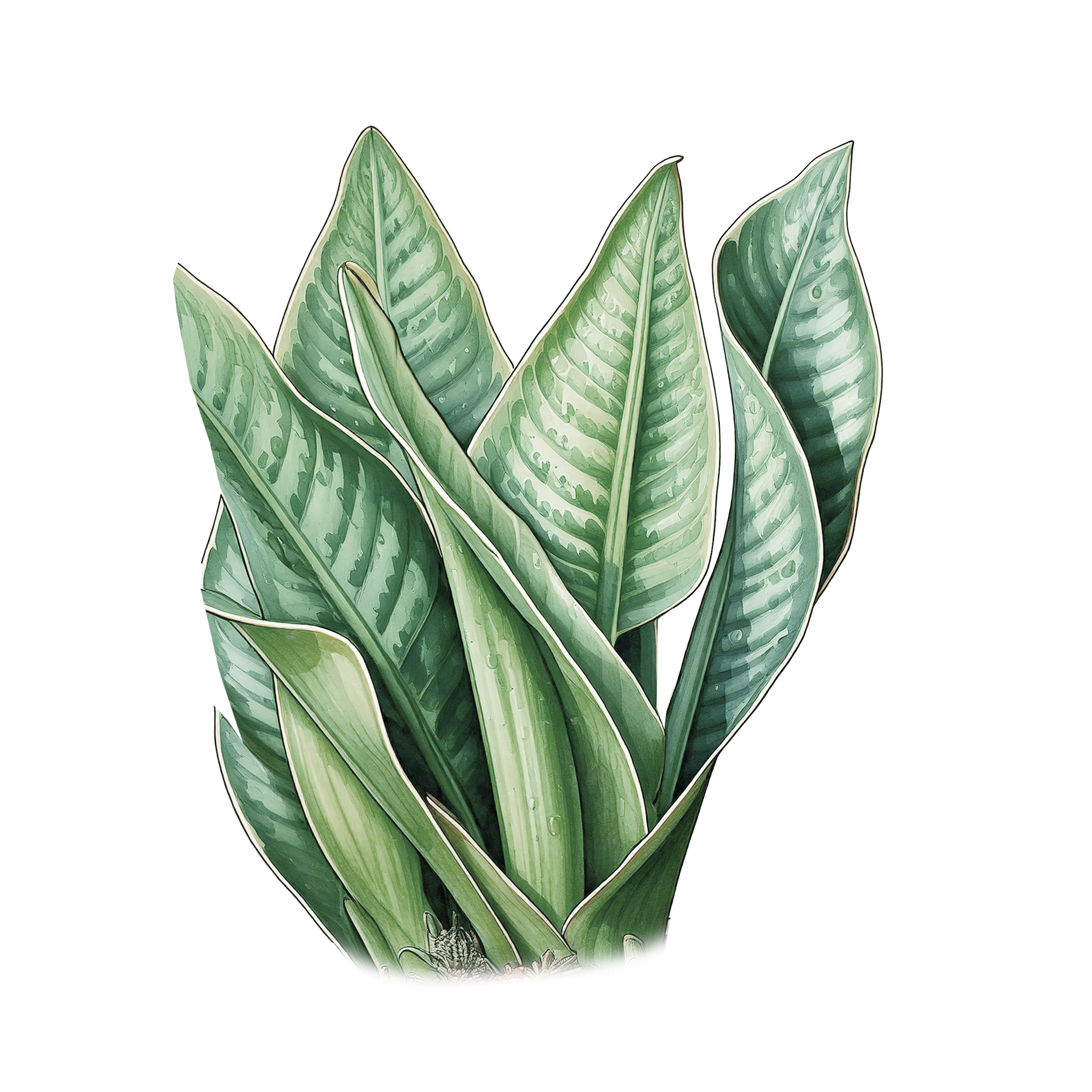
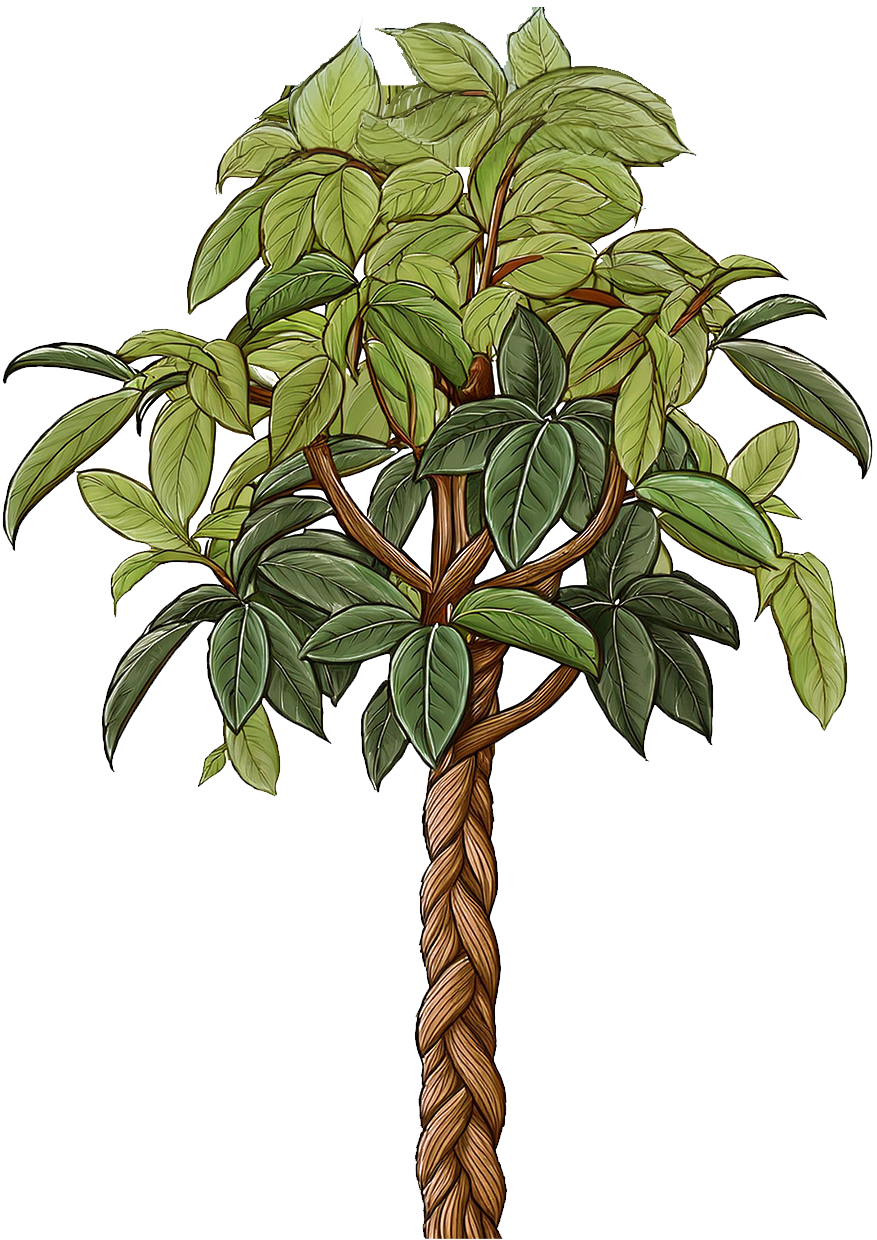





















Baby Snake
Plant
Common Name
Baby Snake Plant, Mother-in-Law's Tongue
Scientific Name
Sansevieria trifasciata 'Laurentii'
Family
Asparagaceae
Native Habitat
Native to West Africa, particularly Nigeria and the Congo.
Description
Leaves are long, upright, sword-shaped. Typically grows to about 12-18 inches tall, though mature plants can reach up to 3 feet. Green leaves with striking yellow edges and horizontal gray-green stripes.
Growing Conditions
Light: Tolerant of low light but thrives in bright, indirect light. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Water less frequently in the winter months.
Humidity: Adaptable to a range of humidity levels; prefers moderate humidity but is drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 15°C - 27°C
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a cactus or succulent mix works well.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally pest-resistant but can be susceptible to mealybugs and spider mites.
Propagation: Can be propagated through leaf cuttings or by division of the rhizomes.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its low maintenance and air-purifying qualities. Ideal for offices, homes, and indoor gardens.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves periodically to remove dust and promote photosynthesis. Rotate the plant occasionally for even growth. Overwatering can lead to root rot.
Kalanchoe
Thyrsiflora
Common Name
Flapjack, Paddle Plant, Desert Cabbage
Scientific Name
Kalanchoe thyrsiflora
Family
Crassulaceae
Native Habitat
Native to Madagascar and Southern Africa.
Description
Kalanchoe thyrsiflora is a striking succulent that adds a unique touch to any indoor or outdoor garden. It has thick, fleshy, paddle-shaped leaves that can grow up to 6 inches long. Leaves are typically a bright green with a reddish margin that intensifies in bright light. They can grow up to 1-2 feet tall. Produces tall flower spikes with clusters of tubular yellow or orange flowers in the late spring and summer.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect sunlight; can tolerate some direct sunlight. Best growth occurs in full sun conditions.
Water: Water thoroughly when the soil is completely dry; avoid overwatering. Reduce watering frequency during the winter months.
Humidity: Thrives in low to moderate humidity; very drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 65°F and 80°F (18°C - 27°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a cactus or succulent mix is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a diluted, balanced fertilizer during the growing season (spring and summer) about once a month.
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally face issues with mealybugs and aphids.
Possible Problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot.
Propagation: Can be propagated easily from leaf or stem cuttings.
Uses
Popular as a decorative house plant due to its unique appearance and ease of care. Often used in succulent gardens and arrangements.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and improve light absorption. Rotate the plant for even exposure to sunlight.
Bird of
Paradise
Common Name
Bird of Paradise, Crane Flower
Scientific Name
Strelitzia reginae
Family
Strelitziaceae
Native Habitat
Native to South Africa
Description
The Bird of Paradise is a stunning and exotic plant that brings a touch of the tropics because of its large, banana-like leaves that can grow up to 18 inches wide and 3 feet long. The leaves are glossy green and arranged in a fan-like pattern, creating a tropical look.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate some direct sunlight. Optimal growth occurs in full sun, especially for flowering.
Water: Water regularly to keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Reduce watering in winter when growth slows.
Humidity: Thrives in moderate to high humidity; can benefit from occasional misting.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 65°F and 70°F (18°C - 21°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a mix designed for tropical plants works well.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs.
Possible Problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot.
Propagation: Can be propagated through division or by seed, though seed propagation can be slow.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant and in landscaping for its dramatic foliage and unique flowers. Often used in tropical-themed gardens and floral arrangements.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure.
Gonialoe
Variegata
Common Name
Variegated Aloe, Aloe Variegata
Scientific Name
Gonialoe variegata (formerly Aloe variegata)
Family
Asphodelaceae
Native Habitat
Native to South Africa, particularly the Eastern Cape region.
Description
Leaves are succulent, fleshy, and lanceolate (spear-shaped) and green in color with distinctive white spots and stripes, giving a variegated appearance. Typically grows to about 12-18 inches tall and can spread wider.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect sunlight but can tolerate some direct sunlight.
Water: Water thoroughly, allowing the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Reduce watering during the winter months.
Humidity: Thrives in low to moderate humidity; very drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 15°C - 27°C
Soil: Well-draining cactus or succulent potting mix; ensure good drainage to prevent root rot.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a diluted, balanced fertilizer during the growing season (spring and summer) once a month.
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally suffer from mealybugs and aphids.
Propagation: Can be propagated through offsets (pups) or leaf cuttings.
Uses
Popular as a decorative houseplant and in succulent gardens. Often used in xeriscaping due to its drought tolerance.
Additional Notes
Ensure good air circulation around the plant to prevent fungal issues. Rotate the plant for even exposure to light.
Satin
Pothos
Common Name
Satin Pothos, Silver Pothos, Scindapsus
Scientific Name
Scindapsus pictus
Family
Araceae
Native Habitat
Native to Southeast Asia, particularly in regions like Indonesia and the Philippines.
Description
Satin Pothos plants are low maintenance plants. They have heart-shaped, thick, and glossy leaves that can grow up to 4-6 inches long. They feature silver or gray variegation on a dark green background, giving it a striking, metallic appearance. Grows as a trailing or climbing vine, making it ideal for hanging baskets or trellises. Can reach lengths of 3-6 feet or more, depending on the growing conditions.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate low light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry; ensure good drainage. Reduce watering in winter when the plant’s growth slows.
Humidity: Thrives in moderate to high humidity but is adaptable to average household humidity.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 65°F and 85°F (18°C - 29°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a standard houseplant mix or aroids mix works well.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by spider mites and mealybugs.
Possible problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves.
Propagation: Can be easily propagated through stem cuttings placed in water or soil.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its attractive foliage and air-purifying qualities. Suitable for indoor spaces, offices, and homes.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves periodically to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure.
Ponytail
Palm
Common Name
Ponytail Palm
Scientific Name
Beaucarnea Recurvata
Family
Asparagaceae
Native Habitat
Eastern Mexico, particularly in the state of Veracruz
Description
A unique plant characterized by a thick, bulbous trunk that stores water, topped with long, slender, arching leaves resembling a ponytail. It typically grows to about 3-6 feet tall
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate some direct sunlight
Water: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Water less frequently in winter
Humidity: Tolerant of low humidity; does well in average household humidity
Temperature: Thrives in temperatures between 15°C - 27°C
Soil: Well-draining cactus or succulent mix is ideal
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a diluted, balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer)
Pests: Generally resistant to pests, but can occasionally attract mealybugs or spider mites
Propagation: Can be propagated from offsets or seeds, though offsets are more common
Uses
Popular as a houseplant due to its unique appearance and low maintenance. Often used in indoor settings and as a decorative element in offices and homes
Additional Notes
Rotate the plant occasionally for even light exposure. Watch for signs of overwatering, as this can lead to root rot. Dust the leaves regularly to keep them clean and maximize photosynthesis
ZZ Plant
Common Name
Zanzibar Gem
Scientific Name
Zamioculcas zamiifolia
Family
Araceae
Native Habitat
Native to eastern Africa, particularly in countries like Tanzania and Kenya.
Description
The Zanzibar Gem is a resilient and visually appealing plant which has thick, glossy, dark green leaves that are oval and waxy in appearance. Leaves grow on stout, upright stems and can reach up to 12 inches long. Grows in a bushy, upright form, typically reaching heights of 2-3 feet. Known for its fleshy rhizomes that store water, making it highly drought-tolerant.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can thrive in low light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can scorch the leaves.
Water: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings; very forgiving if neglected. Reduce watering during the winter months when growth slows.
Humidity: Adaptable to a variety of humidity levels; prefers average household humidity.
Temperature: Thrives in temperatures between 65°F and 75°F (18°C - 24°C)
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a cactus or succulent mix is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize sparingly with a balanced liquid fertilizer every 6-8 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by mealybugs or spider mites.
Possible Problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot, so ensure proper drainage.
Propagation: Can be propagated through leaf cuttings or by dividing the rhizomes.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its attractive foliage and air-purifying qualities. Ideal for indoor spaces, offices, and homes.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves periodically to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure.
Moonshine
Snake Plant
Common Name
Moonshine Snake Plant
Scientific Name
Sansevieria trifasciata 'Moonshine'
Family
Asparagaceae
Native Habitat
Native to West Africa.
Description
Leaves are broad and upright, with a striking silvery-green color. Typically grows to about 2-3 feet tall. The leaves have a smooth texture and are edged with darker green tones.
Growing Conditions
Light: Thrives in bright, indirect light but can tolerate low light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight to prevent leaf burn.
Water: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Water less frequently in the winter months.
Humidity: Adaptable to various humidity levels; prefers moderate humidity but is drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 15°C - 27°C.
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a cactus or succulent mix is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally pest-resistant; however, watch for mealybugs and spider mites.
Propagation:Can be propagated through leaf cuttings or by division of the rhizomes.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its striking appearance and air-purifying qualities. Ideal for homes, offices, and indoor gardens.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth. Overwatering can lead to root rot.
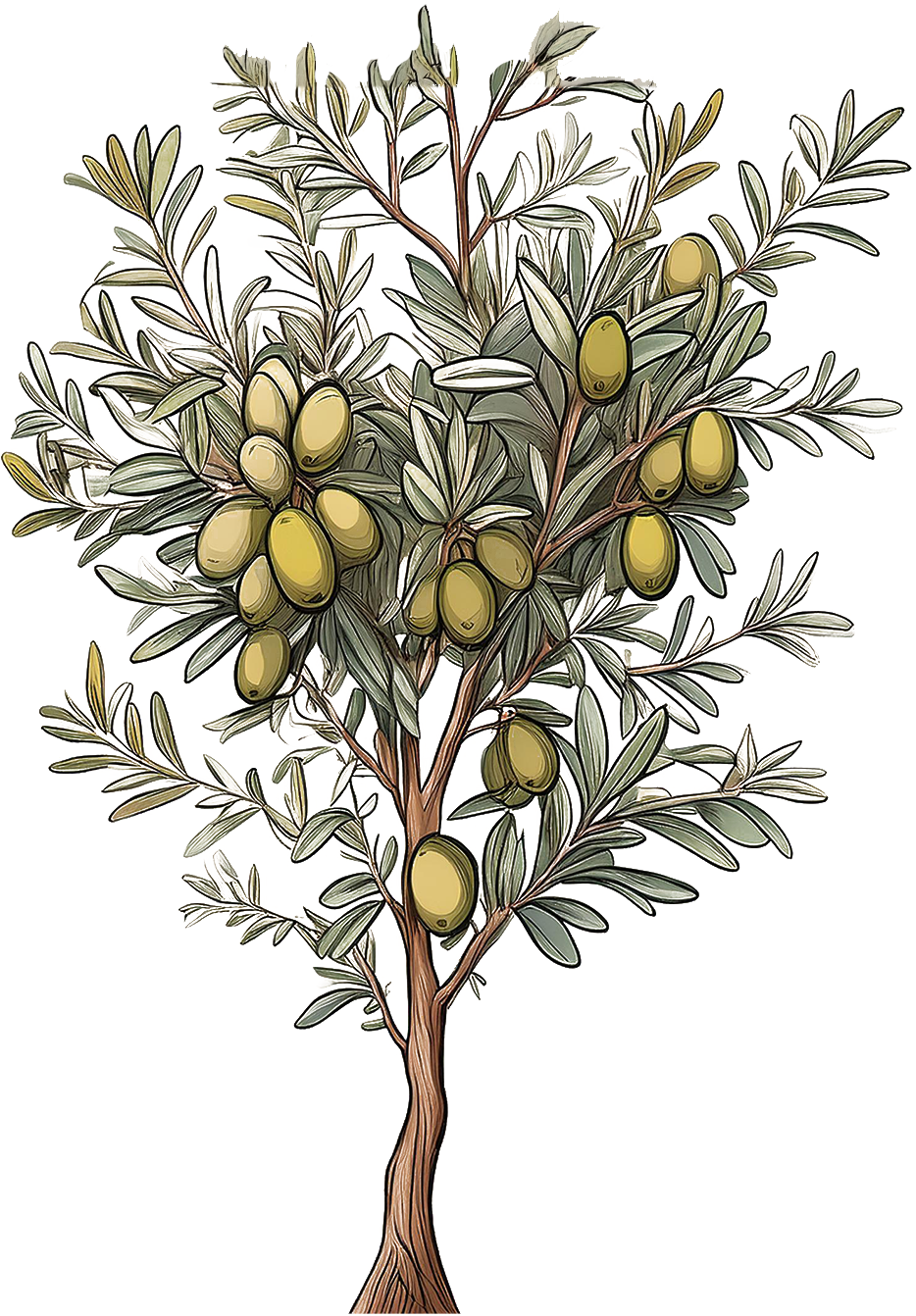
Olive Tree
Common Name
Olive Tree
Scientific Name
Olea europaea
Family
Oleaceae
Origin
Native to the Mediterranean region
Description
Olive trees have narrow, lanceolate leaves that are silvery-green on the underside and dark green on top. Leaves are leathery and typically grow 1-3 inches long. May produce small olives, but often cultivated more for ornamental purposes than fruit production
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers full sun; at least 6 hours of direct sunlight each day is ideal for healthy growth.
Water: Water sparingly; allow the soil to dry out between waterings.
Humidity: Thrives in low to moderate humidity; very drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 60°F and 75°F (15°C - 24°C).
Soil: Prefers well-draining soil; sandy or loamy soil with good drainage is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in the spring to support growth.
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by olive fruit flies and scale insects.
Possible Problems: Watch for signs of overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Propagation: Can be propagated from cuttings or grafting; less commonly from seeds.
Uses
Ideal for container gardening and small spaces, adding Mediterranean ambiance to patios and gardens. Often used as an ornamental plant for its attractive foliage and form.
Additional Notes
Prune regularly to maintain shape and encourage bushy growth. Protect from extreme cold to ensure the health of the tree. Overwatering can lead to root rot, so ensure good drainage.
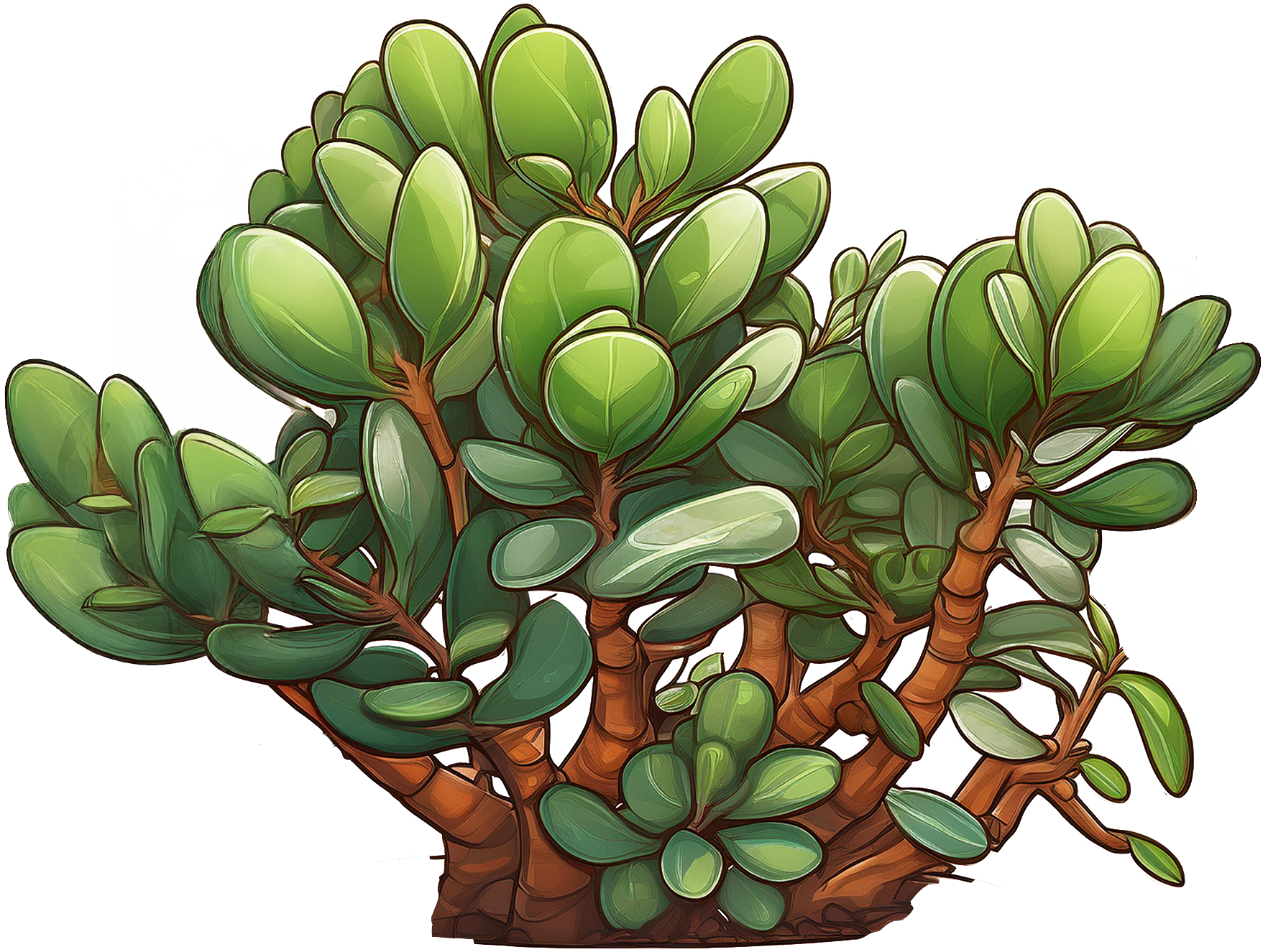
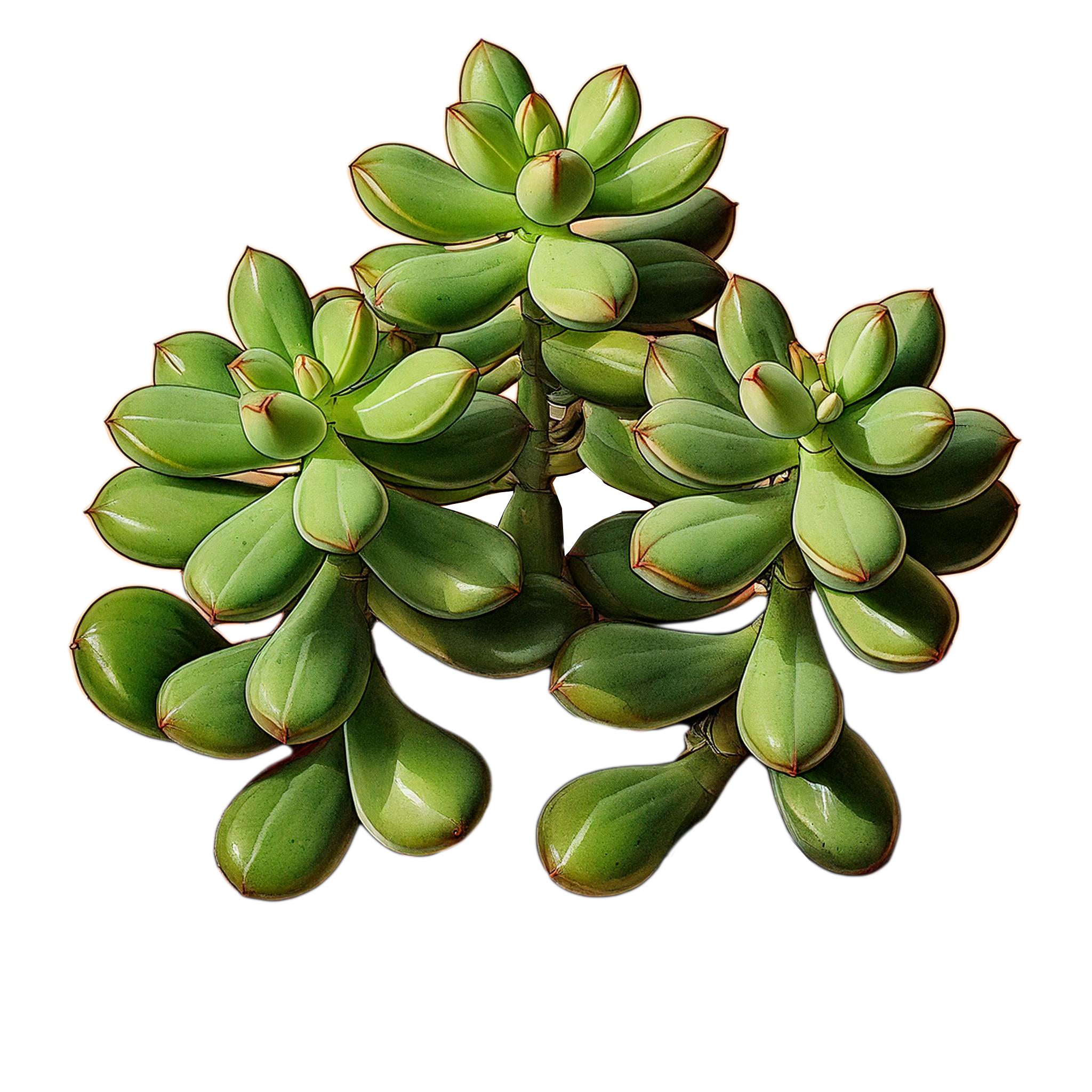
Crassula
Ovata
Common Name
Jade Plant, Money Plant, Friendship Tree
Scientific Name
Crassula ovata
Family
Crassulaceae
Native Habitat
Native to South Africa and Mozambique.
Description
Crassula ovata is a hardy and attractive succulent that has thick, fleshy, oval-shaped leaves that are a vibrant green, often with a glossy appearance. They can develop a reddish tint around the edges when exposed to bright light. They grow as a small shrub that can reach heights of 2-3 feet indoors.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect sunlight but can tolerate some direct sunlight.
Water: Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil is dry; ensure good drainage. Reduce watering in the winter months when the plant is dormant.
Humidity: Adaptable to low humidity; prefers dry conditions typical of succulent environments.
Temperature: Thrives in temperatures between 18°C - 24°C
Soil: Well-draining potting mix.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a diluted, balanced fertilizer during the growing season (spring and summer), about once a month.
Pests: Generally pest-resistant but can occasionally be affected by mealybugs and aphids.
Propagation: Can be easily propagated from leaf or stem cuttings.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its aesthetic appeal and resilience. Often associated with good luck and prosperity in various cultures.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and promote photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure.
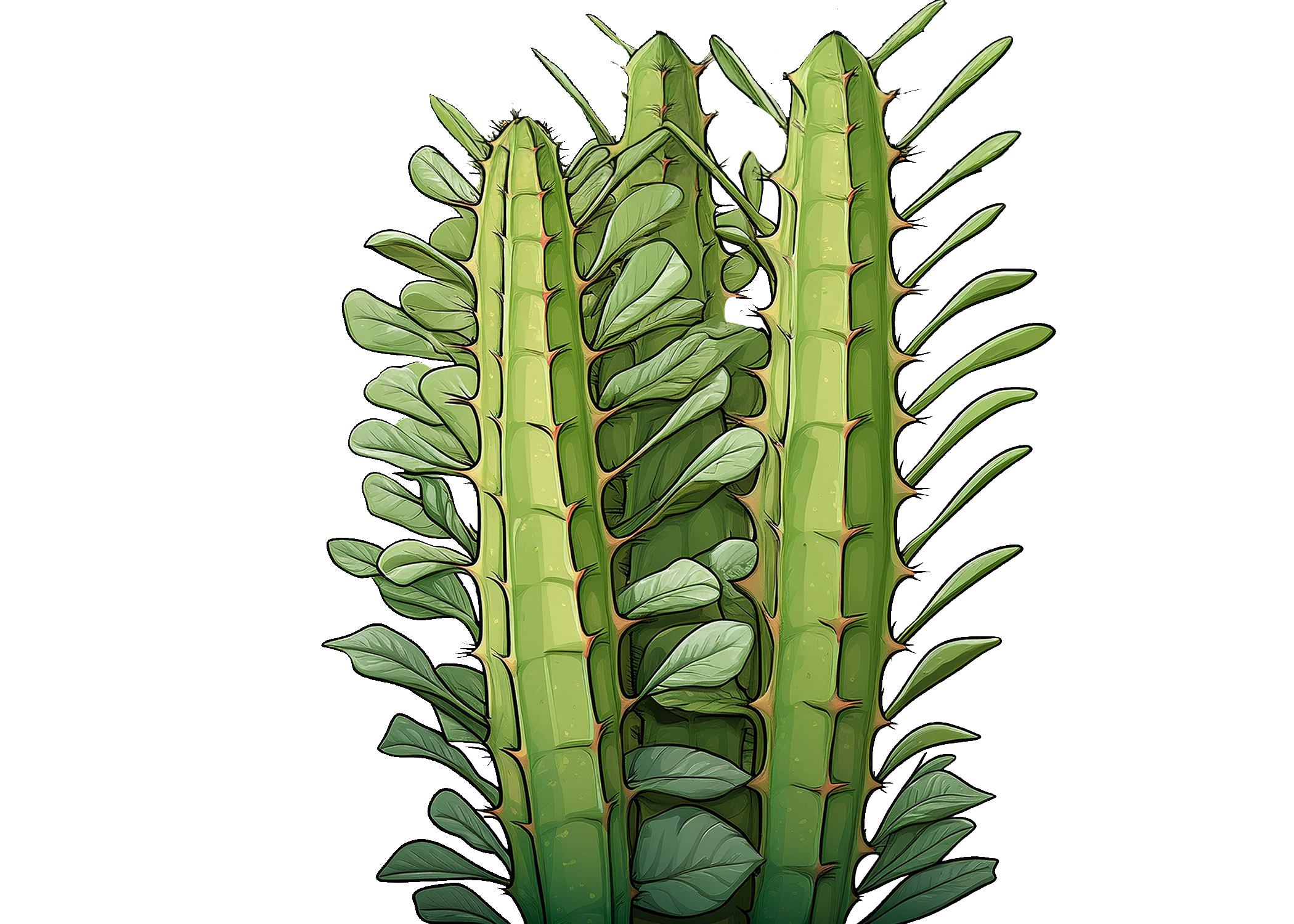
African Milk
Tree
Common Name
African Milk Barrel, Cathedral Cactus, Euphorbia Cactus
Scientific Name
Euphorbia trigona
Family
Euphorbiaceae
Native Habitat
Native to Africa, particularly in countries like Cameroon and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Description
Euphorbia trigona is a distinctive and hardy succulent, has upright stems that can grow up to 6 feet tall or more. The stems have three to five prominent ridges, giving a ribbed appearance. Small, green leaves grow along the edges of the stems, these leaves are typically present on young plants but may drop off as the plant matures.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate some direct sunlight. Ideal for south-facing windows or areas with plenty of natural light.
Water: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings; Water more frequently during the growing season (spring and summer) and reduce in winter.
Humidity: Thrives in low to moderate humidity; very drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 65°F and 80°F (18°C - 27°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a cactus or succulent mix is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a diluted, balanced fertilizer during the growing season (spring and summer), about once a month.
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by mealybugs and scale.
Possible Problems: Beware of overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
Propagation: Can be propagated through stem cuttings, which should be allowed to callous over before planting.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its striking appearance and low maintenance. Often used in succulent gardens and arrangements.
Additional Notes
Wipe stems occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Be cautious when handling, as the sap can be irritating to the skin.
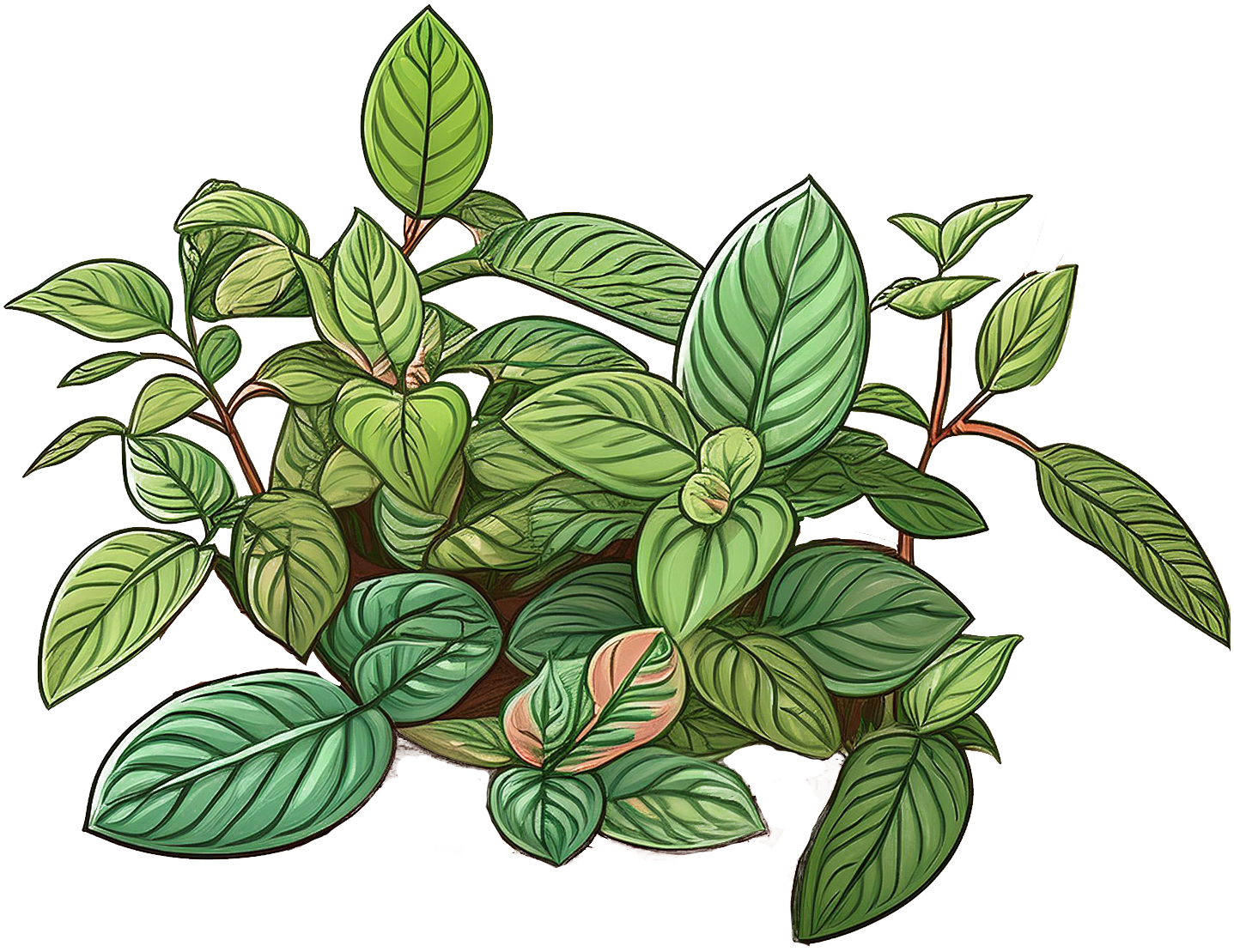
Green
Fittonia
Common Name
Nerve Plant, Mosaic Plant
Scientific Name
Fittonia albivenis
Family
Acanthaceae
Native Habitat
Native to the tropical rainforests of South America, particularly in Peru and Colombia.
Description
Leaves are Small, oval, and about 2-4 inches long. Characteristic veining in white, pink, or red against a deep green background. They typically grow to about 6-12 inches tall.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light. Direct sunlight can scorch the leaves.
Water: Keep the soil consistently moist, but not soggy. Water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
Humidity: Thrives in high humidity. Consider misting or using a humidity tray if the air is dry.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 18°C - 27°C
Soil: Well-draining, rich potting mix. A mix that retains moisture is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a balanced liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Susceptible to pests like spider mites, aphids, and mealybugs.
Propagation: Can be propagated through stem cuttings or division.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its attractive foliage. Often used in terrariums and as a decorative ground cover in tropical gardens.
Additional Notes
Regularly check for pests and remove dead leaves to maintain health. Rotate the plant occasionally for even light exposure. Overwatering can lead to root rot.
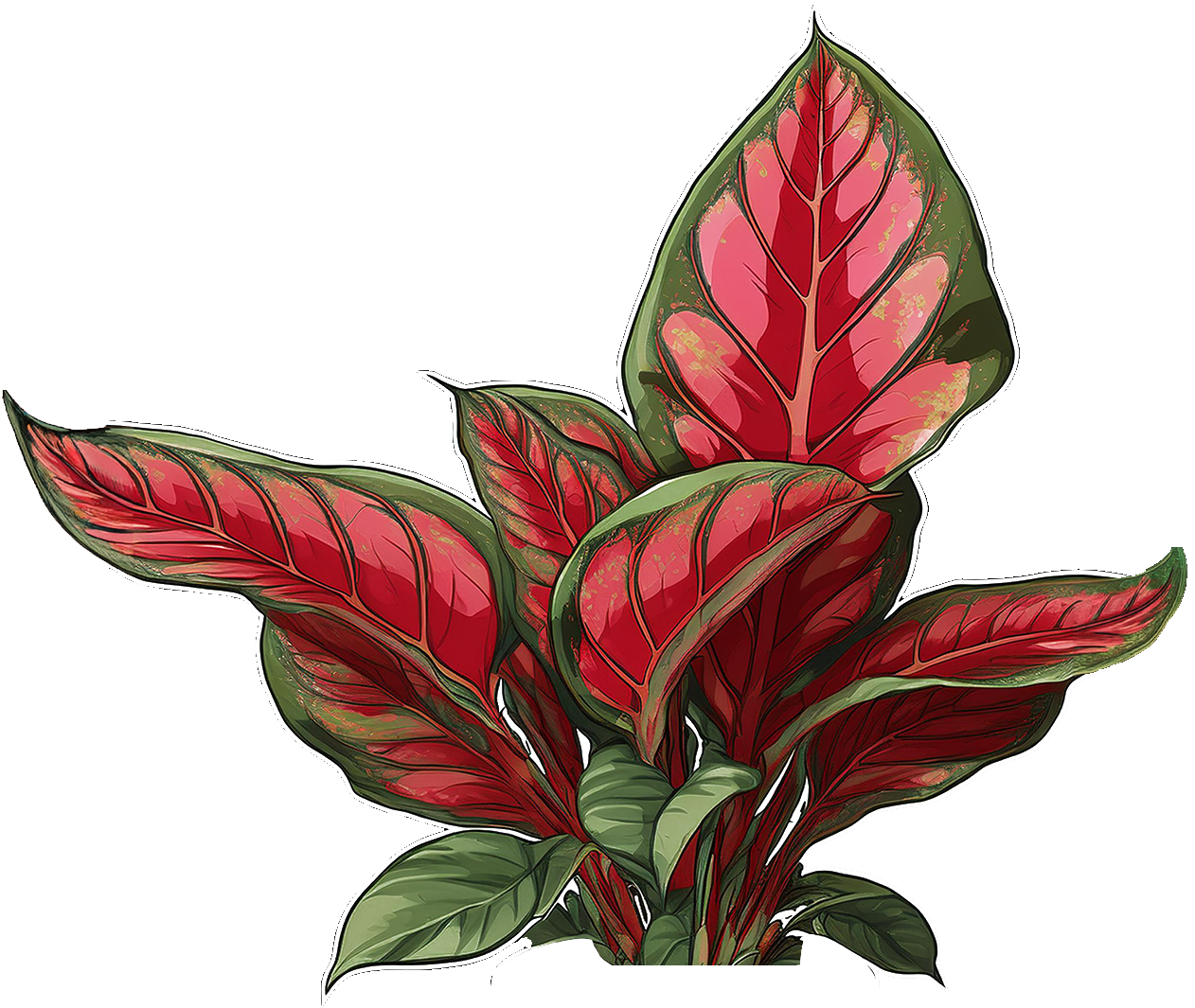
Aglaonema
Red Star
Common Name
Chinese Evergreen 'Favion'
Scientific Name
Aglaonema 'Favion'
Family
Araceae
Native Habitat
Native to tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, particularly Southeast Asia.
Description
Aglaonema 'Favion' is a beautiful and low-maintenance choice for indoor gardening. It has large, lanceolate leaves that can grow up to 6-8 inches long. It features a striking variegation with dark green margins and a lighter green or silvery center, creating a beautiful contrast. Grows upright and bushy, typically reaching heights of about 2-3 feet.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers low to medium indirect light but can tolerate brighter conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry; ensure good drainage. Reduce watering frequency in winter months.
Humidity: Thrives in moderate to high humidity but is adaptable to lower humidity levels.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 18°C - 27°C
Soil: Well-draining potting mix
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced liquid fertilizer every 6-8 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can be susceptible to spider mites, aphids, and mealybugs.
Propagation: Can be propagated through division or stem cuttings.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant due to its attractive foliage and air-purifying qualities. Suitable for indoor spaces, offices, and homes.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves regularly to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant occasionally for even growth.
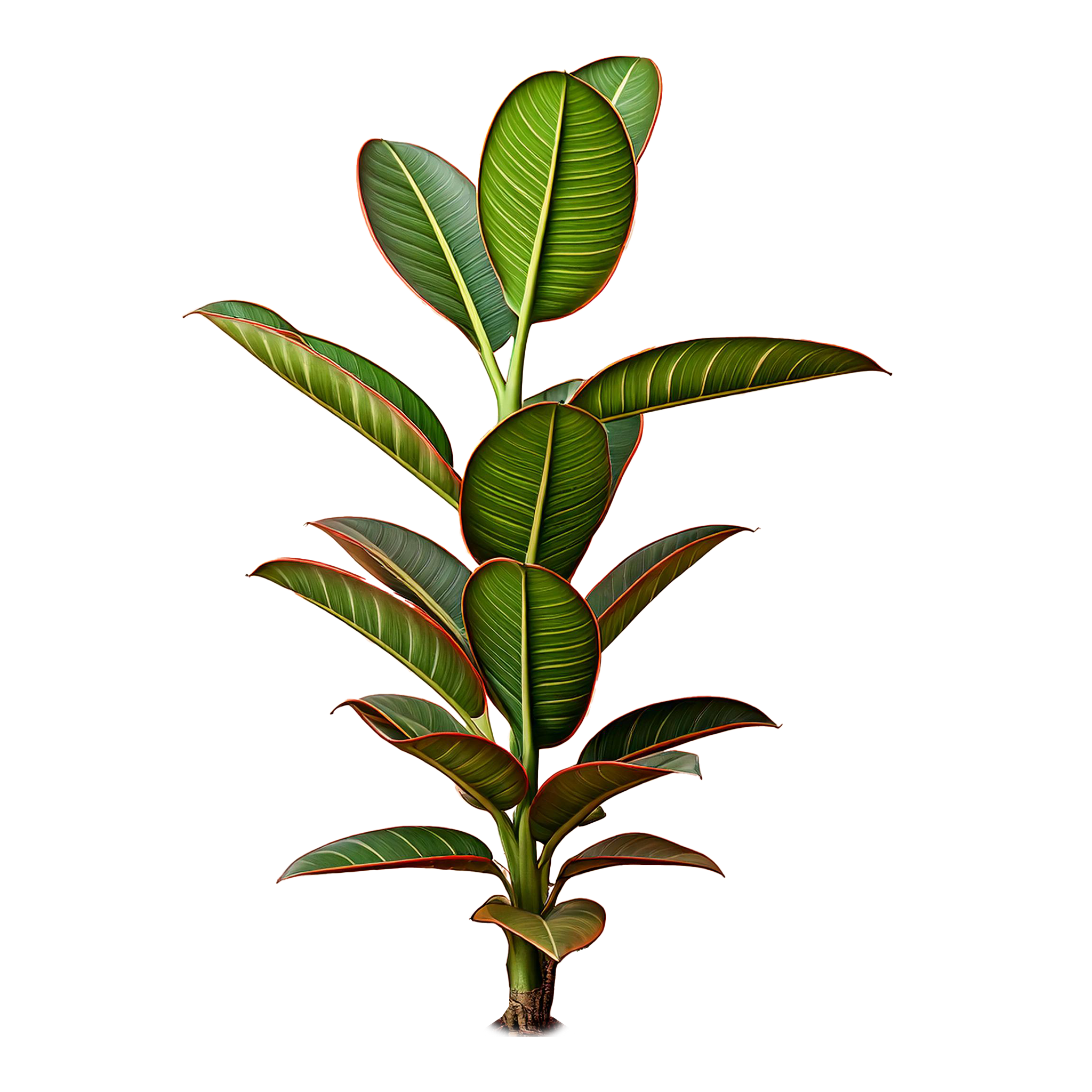
Ruby
Rubber Plant
Common Name
Ruby Rubber Plant
Scientific Name
Ficus elastica 'Ruby'
Family
Moraceae
Native Habitat
Native to Southeast Asia, particularly in tropical rainforests.
Description
Leaves are glossy, broad, and oval-shaped, displaying a beautiful variegation of deep green with pinkish-red edges. Grows up to 3-10 feet tall indoors, depending on conditions.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate some direct sunlight. Insufficient light may cause leaf color to fade.
Water: Allow the top inch of soil to dry out before watering. Reduce watering in the winter.
Humidity: Thrives in higher humidity levels but is adaptable to average home humidity.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 18°C - 24°C.
Soil: Well-draining potting mix with good organic matter.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a balanced liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season.
Pests: Watch for common pests like spider mites and aphids.
Propagation: Can be propagated through stem cuttings or air layering.
Uses
A popular choice for indoor spaces due to its stunning foliage and air-purifying properties. Great for homes and offices.
Additional Notes
Regularly wipe leaves to keep them dust-free and shiny. Rotate the plant for balanced growth. Be cautious of overwatering.
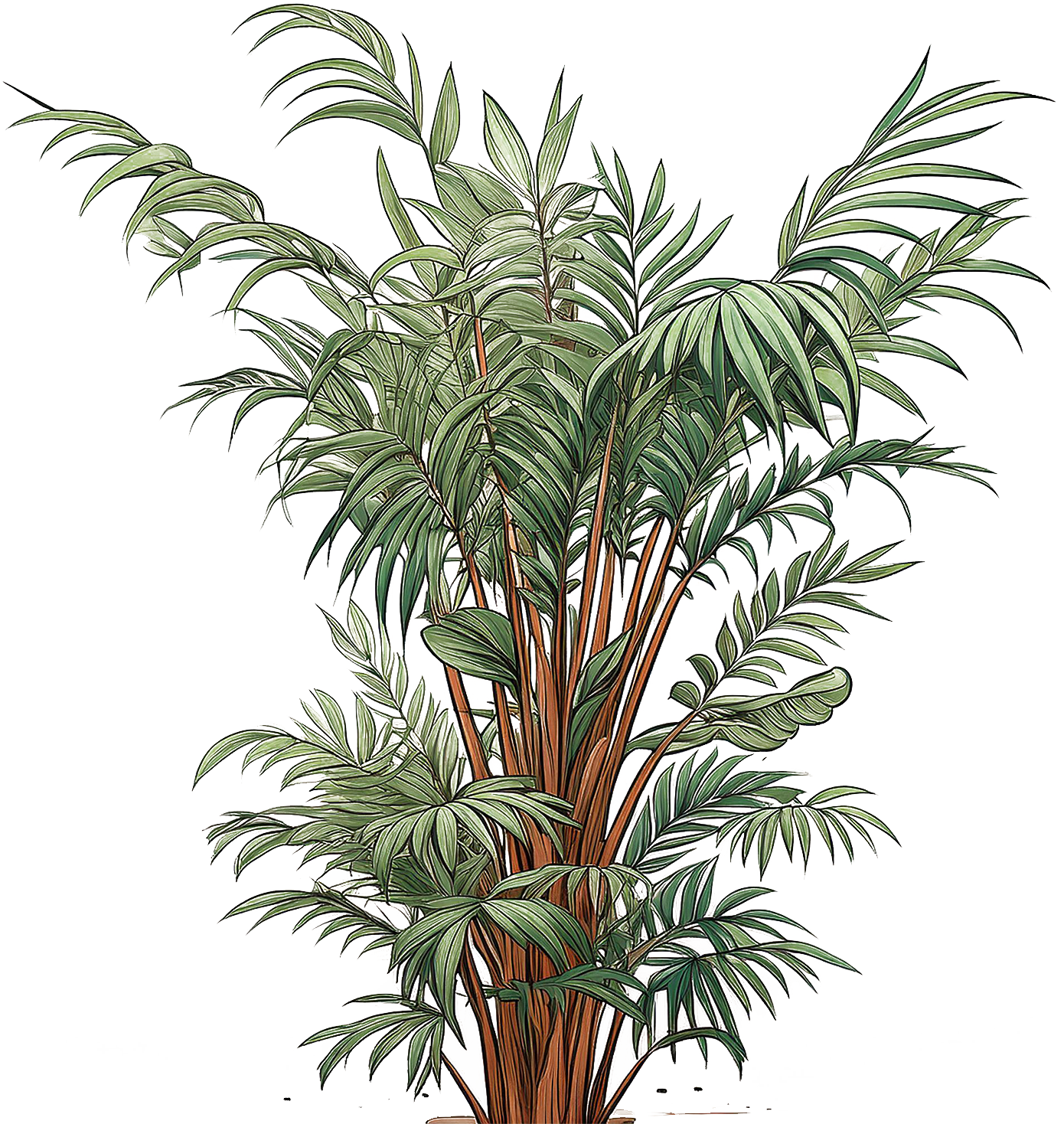
Parlor
Palm
Common Name
Parlor Palm, Neanthe Bella Palm
Scientific Name
Chamaedorea elegans
Family
Arecaceae
Native Habitat
Native to the rainforests of Central America, particularly in Guatemala and Mexico.
Description
Chamaedorea elegans is a classic houseplant that adds a touch of tropical elegance which features slender, arching fronds that are dark green and can grow up to 3 feet long. Each frond is composed of small, leaflets arranged along a central stem, giving a feathery appearance. They grow slowly and can reach a height of 3-6 feet indoors.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers low to bright indirect light; can tolerate lower light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry; ensure good drainage. Reduce watering in the winter months when growth slows.
Humidity: Thrives in high humidity but is adaptable to average household humidity levels.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 65°F and 80°F (18°C - 27°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a standard houseplant mix works well.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by spider mites, mealybugs, and scale.
Possible Problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves.
Propagation: Can be propagated through division or by planting seeds.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant due to its elegant appearance and air-purifying qualities. Suitable for indoor spaces, offices, and homes.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant regularly for even growth and light exposure.
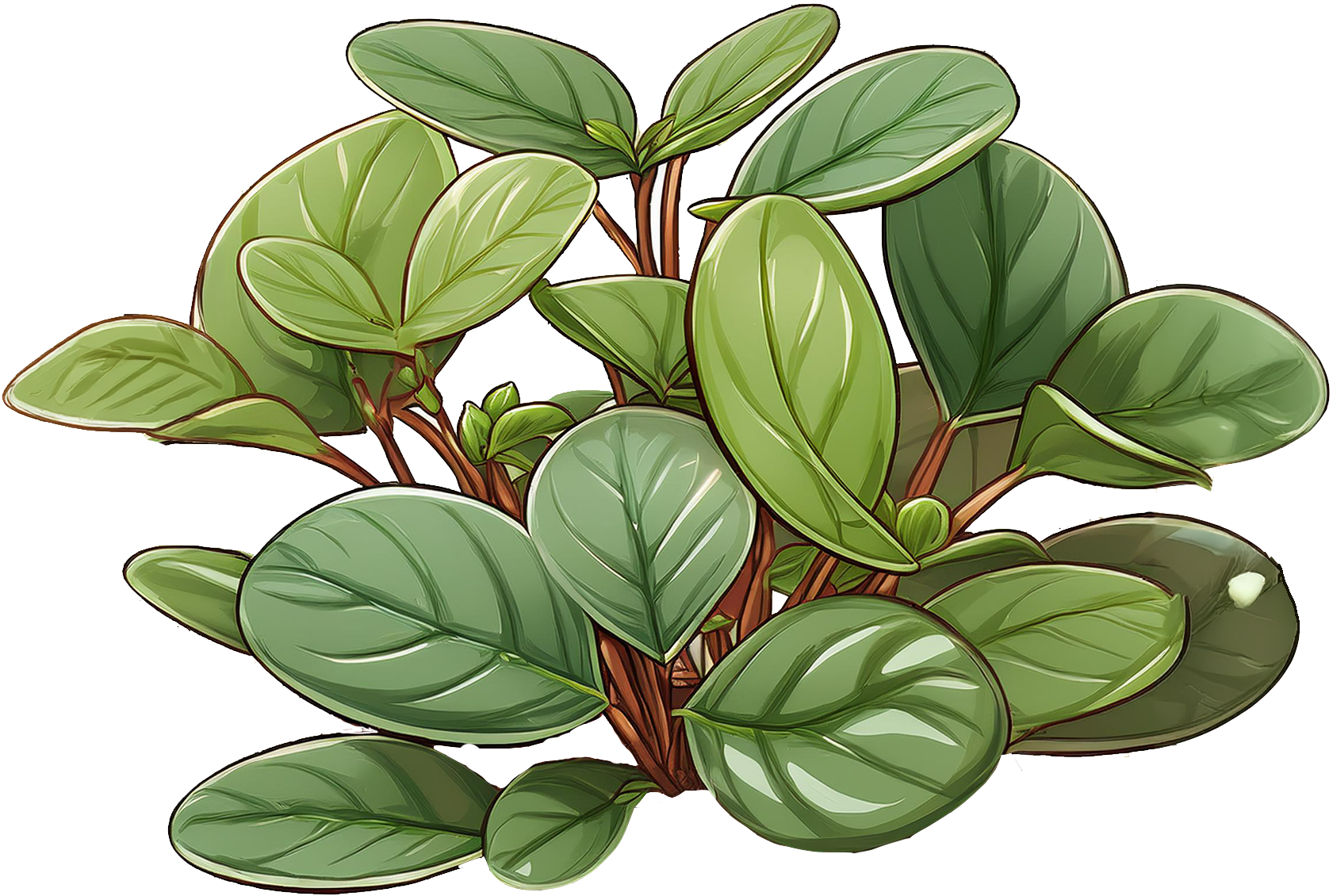
Baby Rubber
Plant
Common Name
Baby Rubber Plant, Pepper Face Plant
Scientific Name
Peperomia obtusifolia
Family
Piperaceae
Native Habitat
Native to tropical regions of Central and South America.
Description
The baby rubber plant is a charming and resilient plant, it has thick, glossy, oval-shaped leaves that can grow up to 4 inches long. Usually deep green, though some varieties may have variegated patterns with cream or lighter green edges.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate low light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry; do not overwater. Reduce watering frequency in winter months.
Humidity: Thrives in moderate to high humidity but is adaptable to lower humidity environments.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 18°C - 27°C
Soil: Well-draining potting mix
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally pest-resistant but can occasionally encounter mealybugs and spider mites.
Propagation: Can be propagated through leaf cuttings or division.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant due to its attractive foliage and ease of care. Ideal for indoor spaces, offices, and homes.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure. Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves.
Lemon
Cypress
Common Name
Lemon Cypress
Scientific Name
Cupressus macrocarpa 'Goldcrest'
Family
Cupressaceae
Native Habitat
Native to California, particularly along the central coast.
Description
Lemon Cypress is an evergreen tree characterized by its vibrant yellow-green foliage, which emits a lemony fragrance when the leaves are crushed. It typically grows to about 3-10 feet tall and has a conical shape.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers full sun to partial shade. Thrives in bright light.
Water: Water regularly, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings.
Humidity: Adaptable to various humidity levels but prefers moderate humidity.
Temperature: Best suited for temperatures between 15°C - 24°C (60°F - 75°F).
Soil: Well-draining, sandy soil is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a balanced fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally pest-resistant, but watch for spider mites and aphids.
Propagation: Can be propagated through seeds or cuttings.
Uses
Popular as a decorative houseplant, in gardens, and for topiary due to its unique appearance and pleasant fragrance.
Additional Notes
Regularly prune to maintain shape and encourage bushier growth. Protect from frost in colder climates.
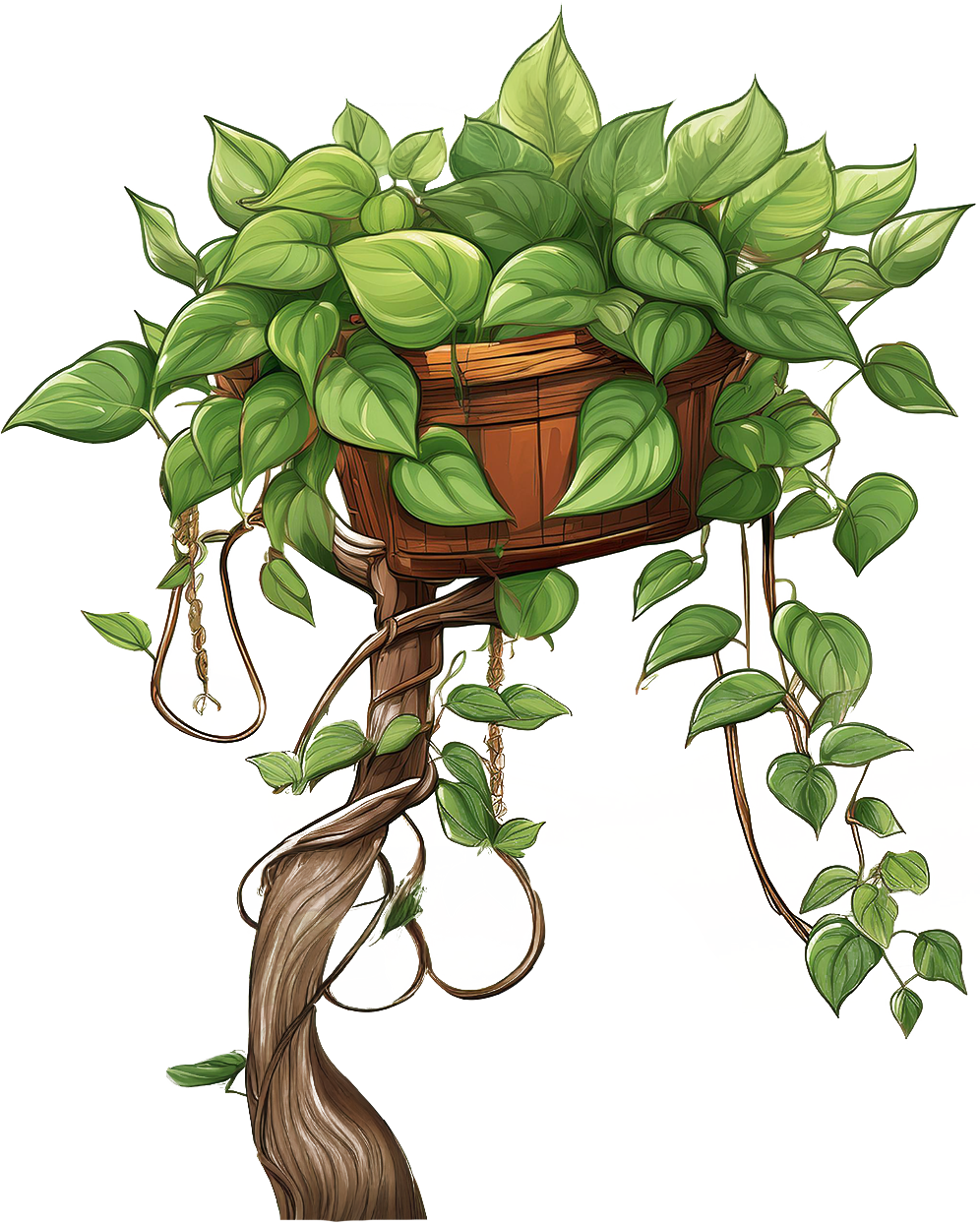
Pothos
'N'Joy'
Common Name
Pothos 'N'Joy', Marble Queen Pothos
Scientific Name
Epipremnum aureum 'N'Joy'
Family
Araceae
Native Habitat
Native to the Solomon Islands, widely cultivated as a houseplant.
Description
Pothos 'N'Joy' is a beautiful and low-maintenance plant. It has heart-shaped, thick, and glossy leaves that are variegated with creamy white and green patterns. Each leaf typically displays a unique marbling effect, making it visually striking. Grows as a trailing or climbing vine, reaching lengths of 2-4 feet or more.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate low light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry; ensure good drainage. Reduce watering frequency during the winter months.
Humidity: Thrives in moderate to high humidity but is adaptable to average household humidity levels.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 65°F and 85°F (18°C - 29°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a standard houseplant mix works well.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by spider mites, mealybugs, and scale.
Possible Problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves.
Propagation: Can be easily propagated through stem cuttings placed in water or soil.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant due to its attractive foliage and air-purifying qualities. Suitable for indoor spaces, offices, and homes.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure.
Hernandez
Sedum
Common Name
Hernandez Sedum
Scientific Name
Sedum hernandezii
Family
Crassulaceae
Native Habitat
Native to Mexico, particularly found in regions with rocky soils.
Description
The Hernandez Sedum features fleshy, green leaves that are often tinged with a reddish hue, especially in bright light. It has a compact growth habit, typically reaching about 4-6 inches in height and spreading up to 12 inches wide. The leaves are thick and oval-shaped, forming a rosette pattern.
Growing Conditions
Light: Thrives in bright, indirect sunlight; can tolerate some direct sunlight but prefers protection from intense afternoon rays.
Water: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings; water less frequently in winter.
Humidity: Prefers low to moderate humidity; very drought-tolerant.
Temperature: Ideal temperatures range from 15°C to 26°C; can tolerate slightly cooler temperatures but should be protected from frost.
Soil: Requires well-draining soil; a cactus or succulent mix is ideal.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Use a diluted, balanced liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests, but watch for mealybugs and aphids.
Propagation: Can be easily propagated from leaf cuttings or offsets.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its striking appearance and low maintenance requirements. Ideal for indoor gardens, rock gardens, and as part of succulent displays.
Additional Notes
Regularly wipe leaves to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth. Be cautious of overwatering, which can lead to root rot. Enjoys being in a sunny spot, making it a perfect choice for bright indoor spaces.
Money
Tree
Common Name
Money Tree, Pachira
Scientific Name
Pachira aquatica
Family
Malvaceae
Native Habitat
Native to Central and South America, particularly in wetlands.
Description
Money trees typically feature glossy, palmate leaves with five to seven leaflets that can grow up to 12 inches long. The leaves are bright green and can appear shiny. Grows as a tree-like plant and can reach heights of 3-6 feet indoors, depending on care.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate lower light conditions. Avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
Water: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry; ensure good drainage. Reduce watering in winter months when growth slows.
Humidity: Thrives in moderate to high humidity; can benefit from occasional misting.
Temperature: Prefers temperatures between 60°F and 75°F (15°C - 24°C).
Soil: Well-draining potting mix; a standard houseplant mix works well.
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced, diluted liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer).
Pests: Generally resistant to pests but can occasionally be affected by spider mites and mealybugs.
Possible Problems: Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves.
Propagation: Can be propagated from seeds or stem cuttings, but it's more commonly grown from seedlings.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant due to its distinctive appearance and air-purifying qualities. Often associated with good luck and prosperity in various cultures.
Additional Notes
Wipe leaves occasionally to remove dust and enhance photosynthesis. Rotate the plant for even growth and light exposure
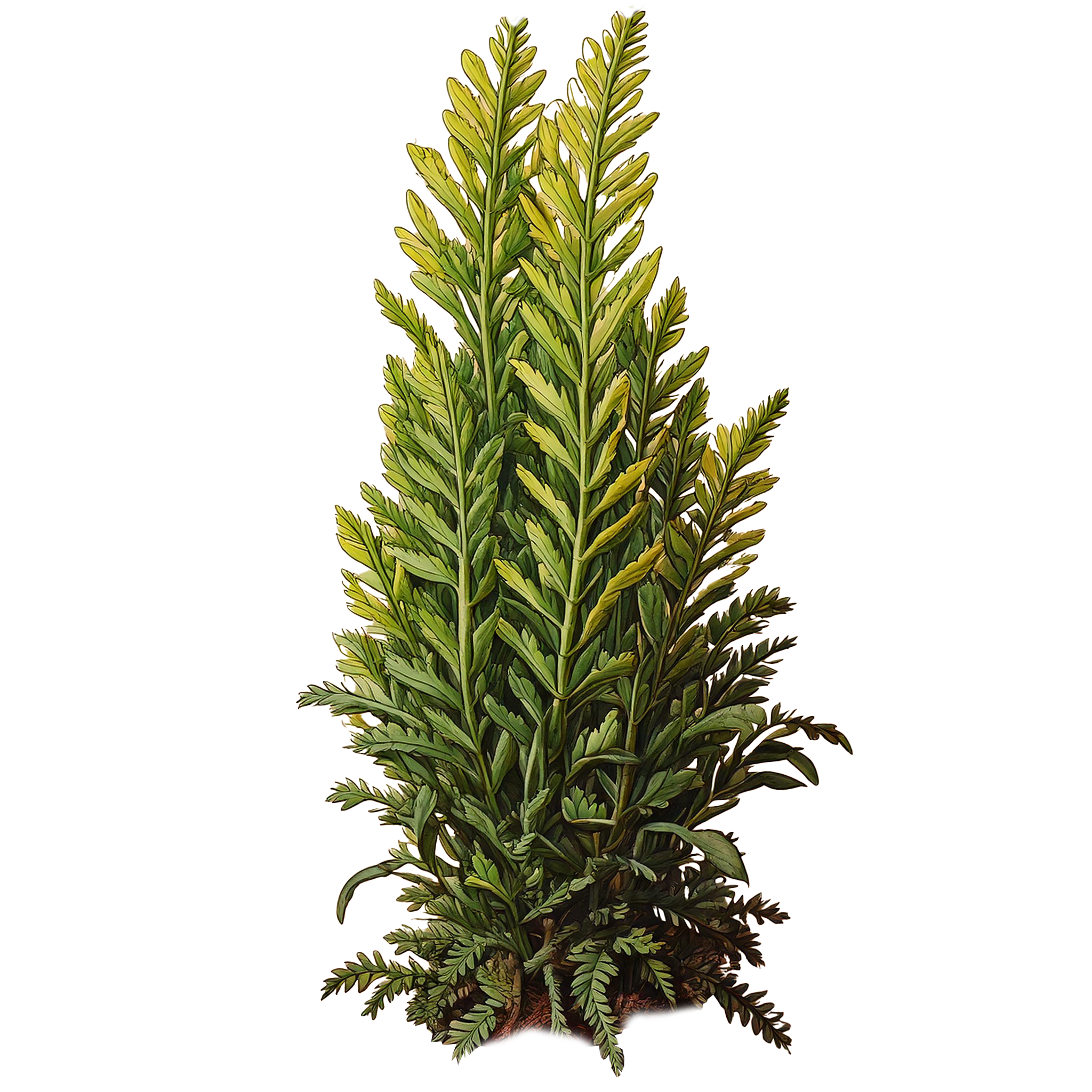
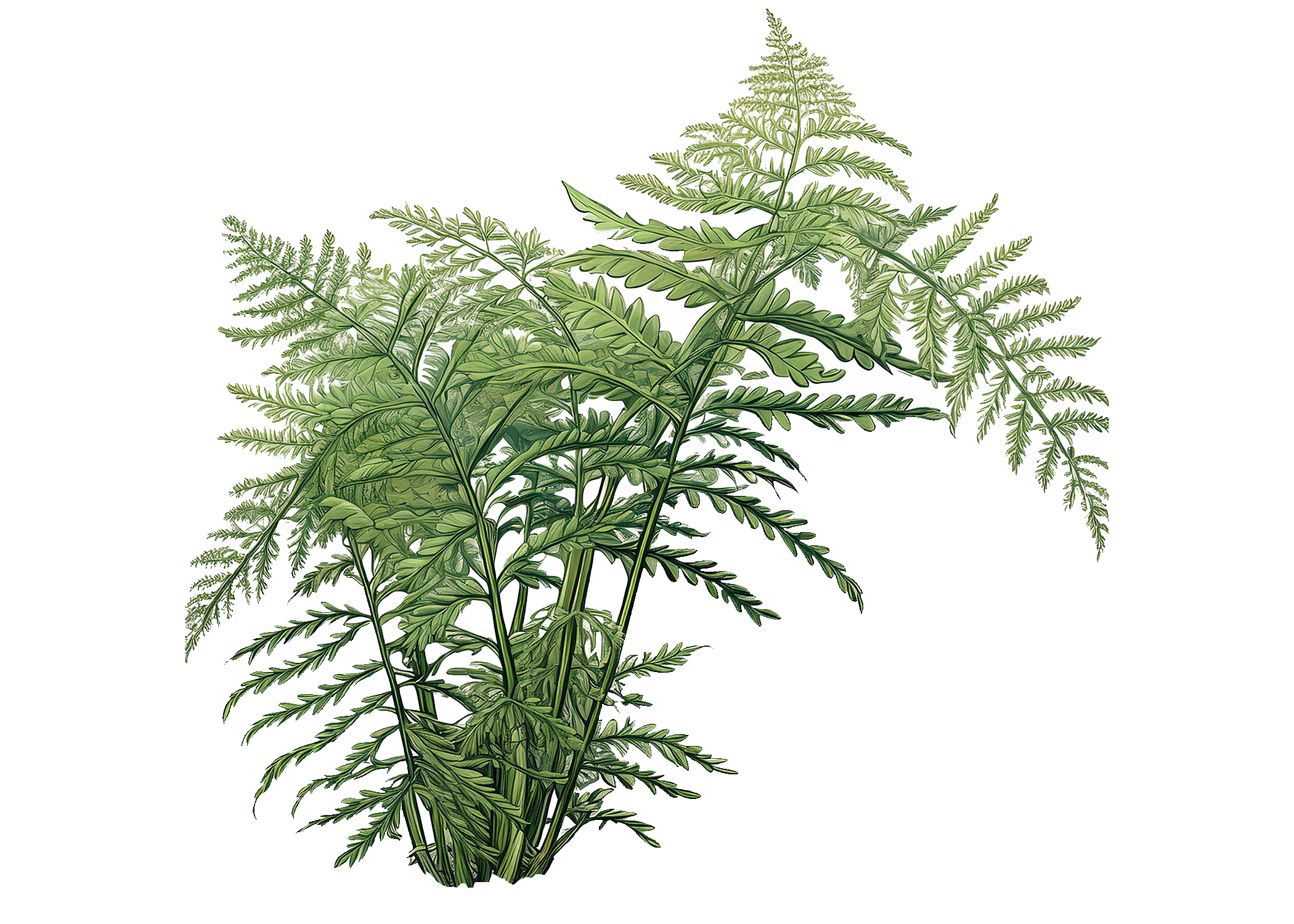
Asparagus
Fern
Common Name
Asparagus Fern, Ferny Asparagus, Sprengeri Fern
Scientific Name
Asparagus densiflorus (formerly Asparagus sprengeri)
Family
Asparagaceae
Native Habitat
Native to South Africa
Description
The asparagus fern is a charming and resilient plant. Leaves feature feathery, needle-like foliage that resembles a fern. The leaves are actually modified stems called cladodes, which give the plant its fern-like appearance. The plant can grow to about 2-3 feet in height and can spread widely.
Growing Conditions
Light: Prefers bright, indirect light but can tolerate some direct sunlight.
Water: Keep the soil consistently moist but not soggy. Water when the top inch of soil feels dry, reducing frequency in winter.
Humidity: Prefers moderate to high humidity; can benefit from occasional misting.
Temperature: Thrives in temperatures between 15°C - 24°C
Soil: Well-draining potting mix
Care Tips
Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced liquid fertilizer every 4-6 weeks during the growing season (spring and summer)
Pests: Susceptible to pests like spider mites, aphids, and scale insects.
Propagation: Can be propagated through division or by planting seeds.
Uses
Popular as a houseplant for its lush foliage and as a decorative plant in hanging baskets. Often used in floral arrangements for its attractive fronds.
Additional Notes
Regularly trim back any dead or yellowing fronds to encourage new growth. Rotate the plant occasionally for even light exposure. Overwatering can lead to root rot and yellowing leaves.